A Case of Psychosis and Elevated AST and ALT
Diagnosis of rhabdomyolysis and liver-related sequelae
- Experts diagnose rhabdomyolysis in patients who have experienced a neuromuscular insult with a sudden increase in CK level, classically greater than five times the upper limit of normal and often greater than 5,000 U/L.
- A muscle biopsy, MRI, or EMG is not needed for diagnosis.
- AST and ALT abnormalities are common in rhabdomyolysis, occurring in 93.1% and 75.0% cases respectively.
- Both AST and ALT are found in different cells throughout the body, including skeletal muscle (most pertinent to our case), red blood cells, and brain cells. AST, however, is found in greater concentrations in skeletal myocytes when compared to ALT. As a result, a ratio of AST:ALT >3 is generally observed in cases of rhabdomyolysis.
Back to the case
In order to definitively diagnose or exclude a case of drug-induced liver injury from either vortioxetine or marijuana, a thorough workup for intrinsic causes of liver disease and a liver biopsy would be needed.
- This patient had an extensive serologic workup for acute and chronic causes of liver disease; hepatitis A, B, C, and E, serum Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), herpes simplex virus (HSV), anti-smooth muscle antibody, anti-nuclear antibody, anti-mitochondrial antibody, acetaminophen level, ceruloplasmin, alpha-1 antitrypsin phenotype, and ferritin levels were normal.
- An abdominal ultrasound with doppler was unremarkable.
- A liver biopsy was not performed due to diagnosis of rhabdomyolysis (given elevated CK level) and improvement with rhabdomyolysis treatment (see below).
- While Wilson Disease should be considered due to patient’s young age and history of psychiatric illness, this is less likely given a normal ceruloplasmin, hemoglobin and bilirubin level, and the lack of a low alkaline phosphatase in comparison to an elevated bilirubin.
- Given an AST:ALT ratio >2, alcoholic hepatitis should also be considered in the differential. However, in alcoholic hepatitis, an elevated bilirubin and leukocytosis is typically present, which was not noted in this case. Furthermore, liver enzyme elevations in the thousands, as seen in this case, are not seen in alcoholic hepatitis (Don’t forget the most common cause of transaminases in the thousands for hospitalized patients).
- COVID-19 should also be a consideration as it can cause AST>ALT liver enzyme elevations.
Given the significant elevation in CK, rhabdomyolysis is the most likely cause of abnormal liver enzymes.
Natural history of liver-related sequelae
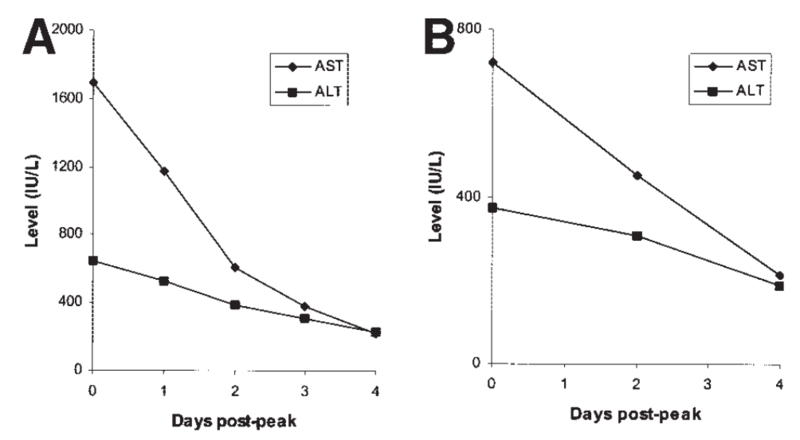
Treatment of rhabdomyolysis entails aggressive fluid resuscitation. The AST and ALT should improve as the CK improves and the muscle injury resolves. It is important to remember that AST has a shorter half-life (~17 hours) than ALT (~47 hours)—because of this difference, the AST levels improve faster than the ALT levels (Figure 1), and the AST:ALT ratio will change as the patient's disease course improves.
Figure 1: Changes in AST and ALT levels after their peak in a case series of muscle injury patients.
ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase. Taken from: Nathwani, R, et al. Serum Alanine Aminotransferase in Skeletal Muscle Diseases.Hepatology 2005. 41(2): 380-382.
Figure 2: Decreases in AST mirror decreases in CK as rhabdomyolysis is treated.
Triangles are ALT values, squares are AST values, and diamonds are CK values. CK: creatine kinase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase. Taken from: Weibrecht, K, et al. Liver Aminotransferases are Elevated with Rhabdomyolysis in the Absence of Significant Liver Injury. J Med Toxicol 2010. 6:294-300.
- Another important point to keep in mind: The transaminase increase is not a result of liver injury, but rather skeletal muscle injury.
- As the patient continues to improve, serial liver chemistry tests should be performed to ensure improvement in the AST and ALT values. Liver chemistry tests should be checked after resolution of the rhabdomyolysis to document normalization of the AST and ALT values.